by Steve Tilson
January 4, 2018
A compromised processor is one of the most serious attack vectors on all Microsoft, Apple, and Linux systems. The recent discovered hardware bugs known as “Spectre & Meltdown” affect modern processors uniquely by accessing information found in the system’s memory. This Dashboard can provide insight to which systems are prone to the new vulnerability.
The new bugs are considered side channel attacks since they use side channels to obtain the information from the accessed memory location. Spectre allows an application to force another application to access arbitrary portions of its memory, which can then be read through a side channel. This unique side channel attack is done by speculative execution, a technique used by high-speed processors in order to increase performance by guessing likely future execution paths and preemptively executing the instructions in them. Spectre takes advantage of this execution and affects all modern processors capable of keeping instructions in flight.
Furthermore, memory isolation is a cornerstone of security and the environment that allows multiple processes to be run on a device. The Meltdown bug allows any application to access all system memory including memory allocated to the kernel and overcomes the memory isolation. The unique side channel attack is one side effect caused by out-of-order execution that is used as a performance enhancement for processors. Meltdown specifically affects every Intel processor on all desktop, laptop and cloud computers except Intel Itanium and Intel Atom before 2013.
SecurityCenter provides information on all outstanding patches for each operating system and a criticality assigned to each vulnerability found. This information can assist all levels and teams in infrastructure and security by targeting systems that hold a higher probability of being compromised.
The report and elements are available in the SecurityCenter Feed, a comprehensive collection of dashboards, reports, assurance report cards and assets. The report can be easily located in the SecurityCenter Feed under the category Threat Detection & Vulnerability Assessments.
The report requirements are:
- SecurityCenter 5.2.0
- Nessus 6.11.2
Tenable SecurityCenter Continuous View® (SecurityCenter CV™) provides continuous network monitoring, vulnerability identification and security monitoring. SecurityCenter CV™ is continuously updated with information about advanced threats, zero-day vulnerabilities and new types of regulatory compliance configuration audit files. Tenable constantly analyzes information from unique sensors, delivering continuous visibility and critical context, and enabling decisive action that transforms a security program from reactive to proactive. Active scanning periodically examines the applications on the systems, the running processes and services, web applications and configuration settings. Passive listening provides real-time discovery of vulnerabilities on operating systems, protocols, network services, wireless devices, web applications, and critical infrastructure. SecurityCenter CV™ provides an organization with the most comprehensive view of the network and actionable information to support mitigation efforts and reduce cyber risk. All levels can better monitor and asses patch management efforts for Spectre & Meltdown bugs happening across the network with SecurityCenter CV™. Tenable enables powerful, yet non-disruptive, continuous monitoring that will provide organizations with the information needed to reduce risk within the enterprise.
This dashboard contains the following components:
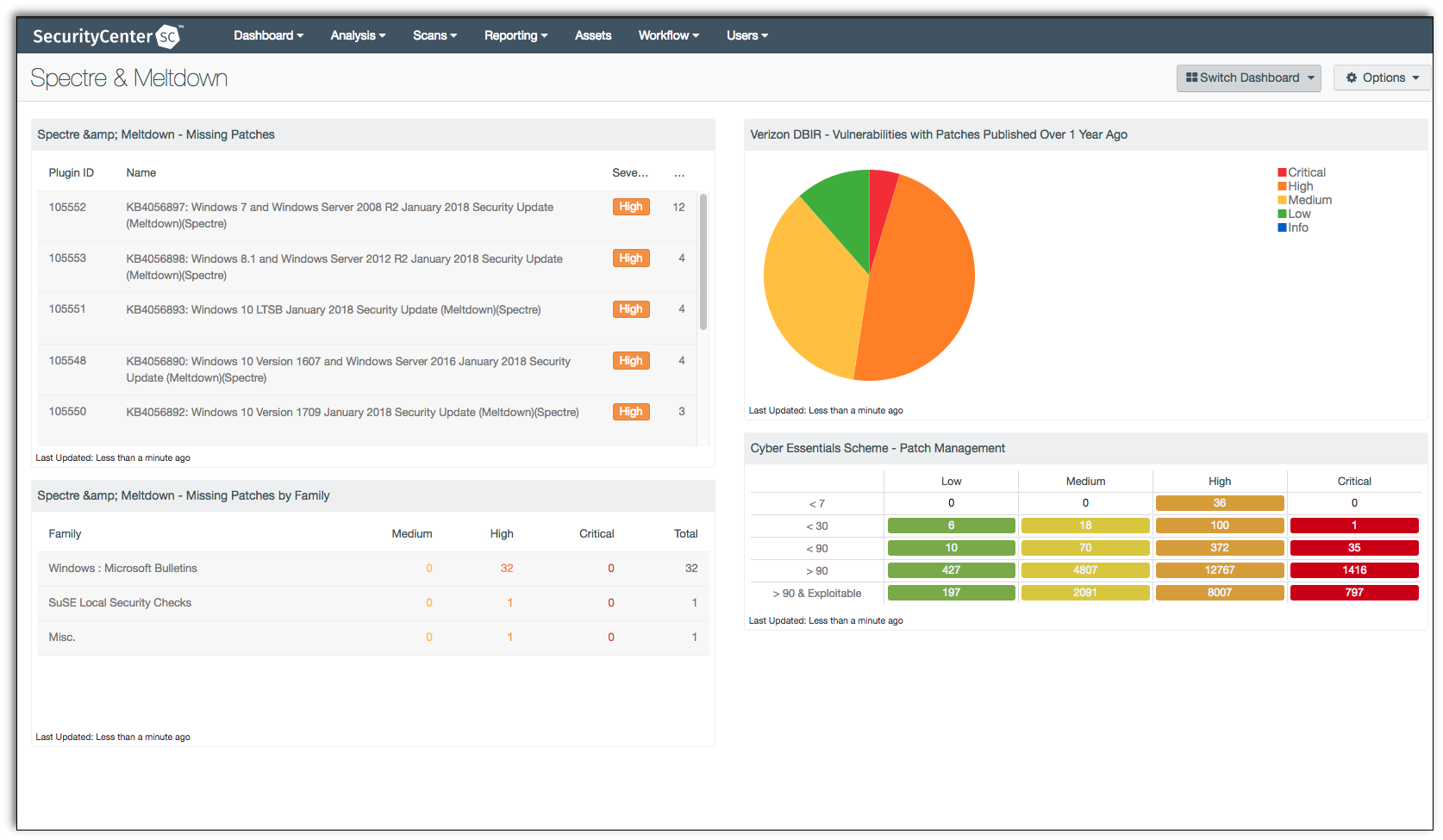
Spectre & Meltdown - Missing Patches: The Missing Patches component is a table that provides a summary of the top 10 vulnerabilities in relation to CVE-2017-5753, CVE-2017-5715, and CVE-2017-5754. The summary includes the Plugin ID used, the Name, Severity, and total found.
Vulnerabilities with Patches Published Over 1 Year Ago: The Vulnerabilities with Patches Published Over 1 Year Ago component is a pie chart that provides a quick snapshot of the vulnerabilities in the organization. The vulnerabilities in the pie chart have patches that have been published over one year ago.
Missing Patches by Family: The Missing Patches by Family component is a table that provides a summary of the top 20 medium, high, and critical vulnerabilities in relation to CVE-2017-5753, CVE-2017-5715, and CVE-2017-5754 by the family plugin.
Patch Management: Patch Management component is a matrix that provides a summary of vulnerabilities and patch release dates. The dates are summarized with 7, 30, 90, more than 90 days, and more than 90 days and exploitable. The matrix provides columns for each severity, ranging from low to critical.